Earth Day 2020: Helping Smallholder Farmers Build Climate Resilience
Join TechnoServe in celebrating Earth Day with stories of climate resilience from our work in Africa, India, and Latin America. Take our quiz to test your knowledge on how climate change impacts smallholder farmers, then read stories about some of the small-scale producers who are using training from TechnoServe to improve their climate resilience and their lives.
April 22 marks the 50th anniversary of Earth Day — a time to inspire action and recognize our shared responsibility for protecting the planet. Although Earth Day started as a movement in the United States, it soon moved global and is now considered the world’s largest civic event.
At TechnoServe, we recognize that smallholder farmers around the world are on the front lines of this global challenge. These farmers are the first to be impacted by climate change, but are often the least prepared to fight it. Without resources to combat threats like extreme weather, worsening natural disasters, and crop and livestock diseases, these small-scale producers earn lower incomes and face higher risks as they struggle to earn a living. To solve this challenge, we must address the root causes of climate change, but also help farmers adapt to the already changing climate.
Celebrate Earth Day with TechnoServe by…
Taking Our Quiz
Test your knowledge about how climate change impacts smallholder farmers. After the quiz, you’ll learn some of the ways TechnoServe is helping these farmers cope with a changing climate. How much did you know?
Learning About Climate Change
Learn five ways climate change is threatening the livelihoods of smallholder farmers. Although climate change is a global threat, its effects will be felt differently around the world. Climate change is already impacting the daily lives of smallholder farmers — from the money they earn from their crops to the food they put on the table for their families.
Getting Inspired
Read stories of farmers who are fighting back against climate threats and improving their local environments after participating in TechnoServe trainings.
In Ethiopia, we caught up with Mudhin Mohammed, manager of the Nasir Mohammed coffee hulling station. Hulling stations are an essential part of coffee communities, serving as centralized collection centers where the parchment layer that separates the well-known bean from the exterior cherry fruit is removed. However, removing the parchment layer leaves behind woody husks that pose a serious fire hazard and can contaminate local water sources. TechnoServe worked with Nasir Mohammed to transform coffee husks from a safety risk to an important source of mulch for local coffee farmers, benefitting both the environment and surrounding communities.
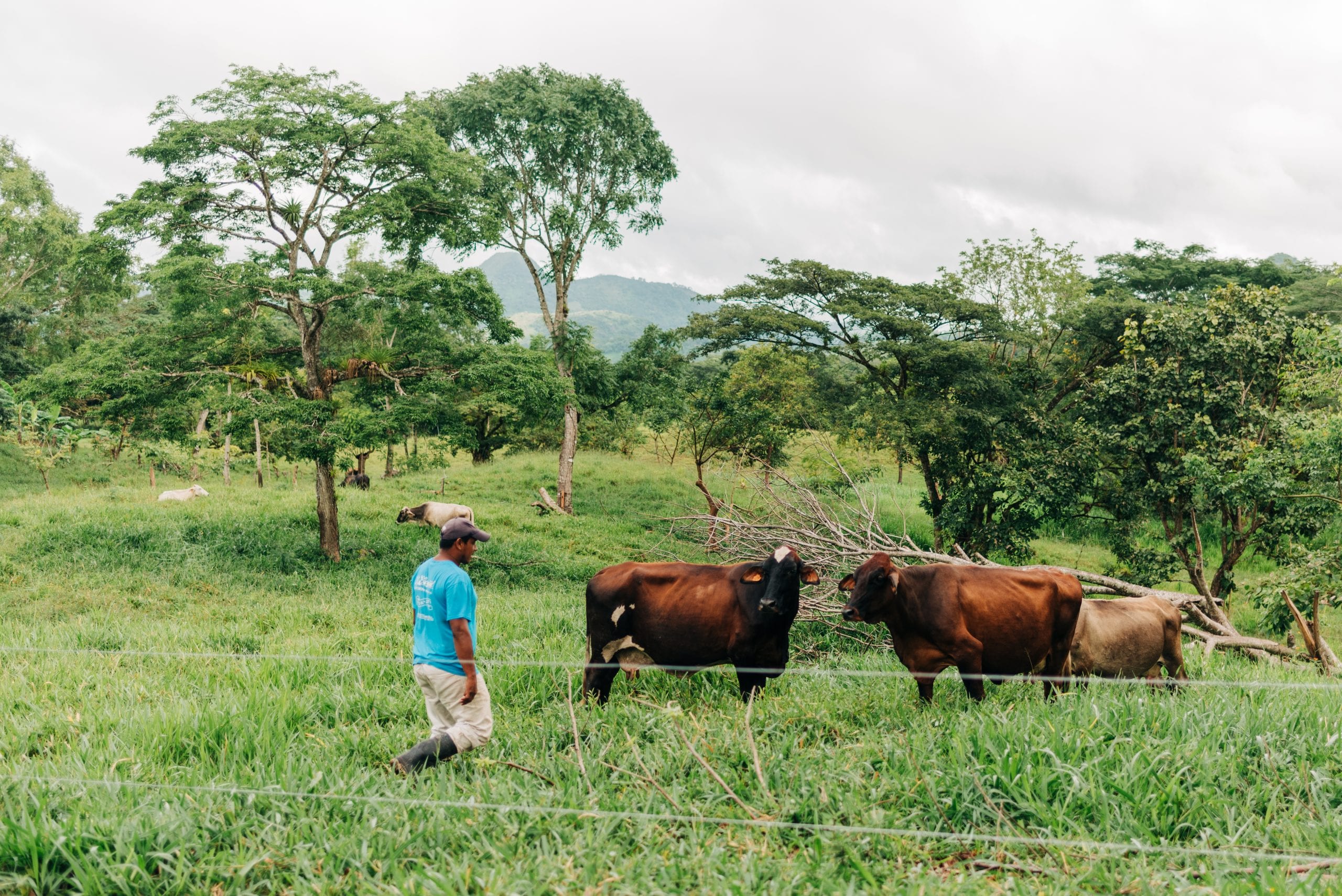

In Nicaragua, cattle ranchers like Jeudin Francisco Mendoza Martinez are learning techniques to help them cope with shifting weather and precipitation patterns, ensuring that their cattle will have enough forage to remain healthy and productive, even during prolonged dry seasons. Through the program, ranchers learn how to adopt intensive silvopastoral systems, which encourage the integration of trees, bushes, and grasses into grazing land.
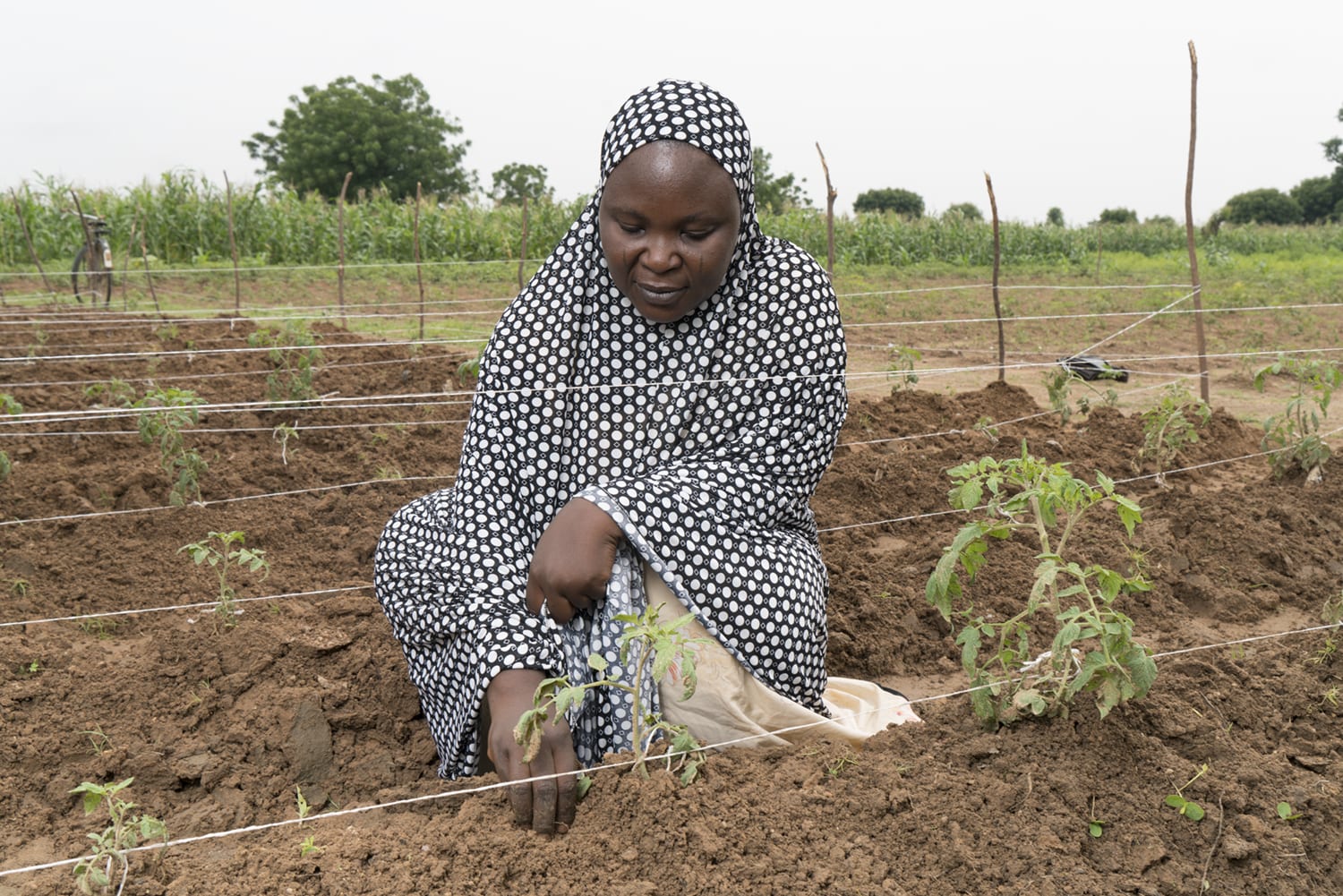

In Nigeria, farmers are using climate-smart techniques to reduce post-harvest losses. Traditional efforts to improve food security have focused on increasing agricultural yields and introducing technologies to reduce post-harvest losses. However, the effects of climate change – including increased soil salinity, extreme temperatures, changes in moisture content, and the unavailability of suitable tomato seed varieties – have made it difficult to increase and sustain year-round tomato production. TechnoServe is teaching these farmers about good agricultural practices, production staggering, zero-energy cooling, and improved seed varieties, helping them improve yields and reduce post-harvest losses in the face of climate threats.




